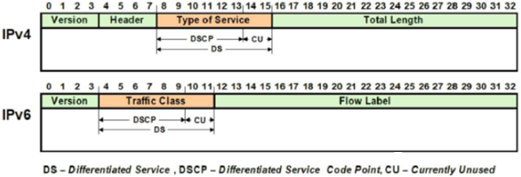
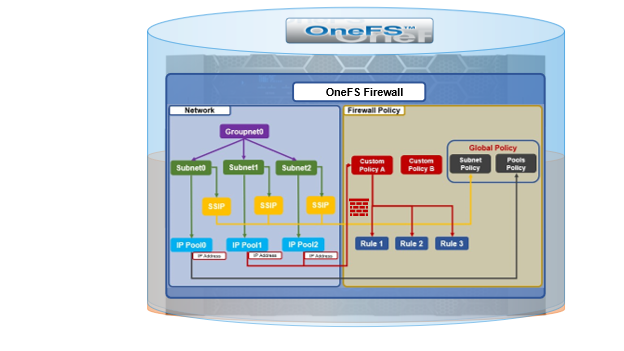
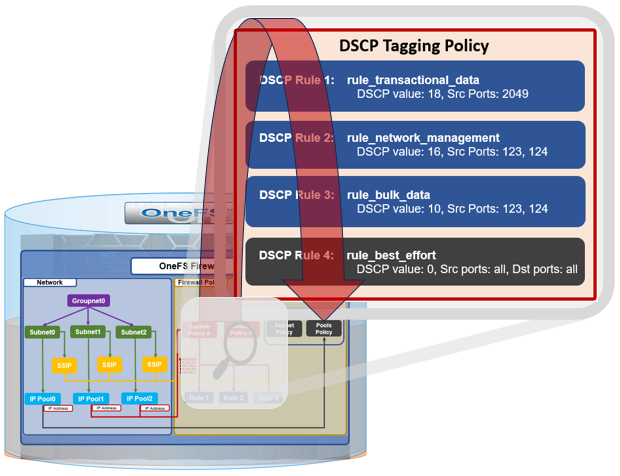
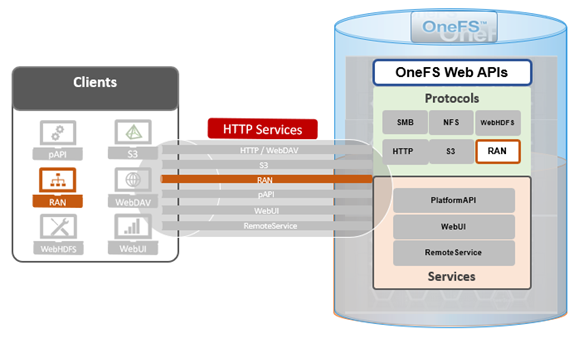
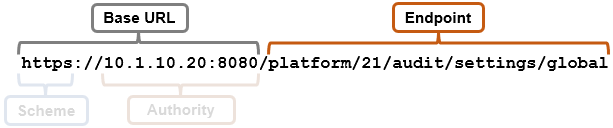
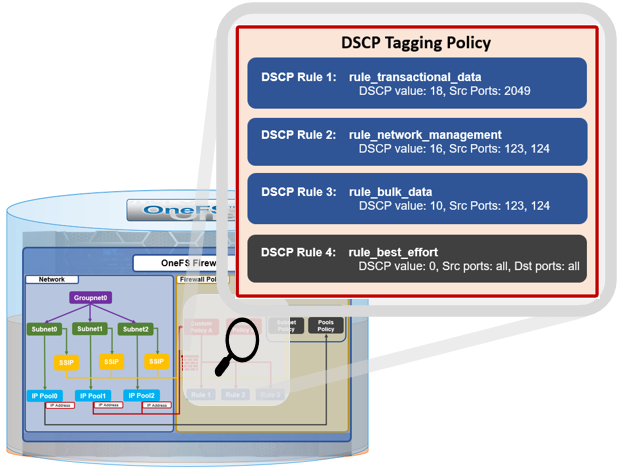
As we saw in the previous article in this series, OneFS 9.9 introduces support for DSCP marking, and the configuration is cluster-wide, and based on the class of network traffic. This is performed by the OneFS firewall, which inspects outgoing network traffic on the front-end ports and assigns it to the appropriate QoS class based on a set of DSCP tagging rules:
Configuration-wise, DSCP requires OneFS 9.9 or later, and is disabled by default – both for new installations and legacy cluster upgrades. The QoS feature can be configured through the CLI, WebUI, and pAPI endpoints. And for clusters that are upgrading to OneFS 9.9, the release must be committed before DSCP configuration can proceed.
Before enabling DSCP tagging, verify the current firewall and DSCP settings:
# isi network firewall settings view Enabled: True DSCP Enabled: False
Update these as required, remembering that both the firewall and DSCP must be running in order for QoS tagging to work. DSCP is off by default, but can be easily started with the following CLI syntax:
# isi network firewall settings modify dscp-enabled true
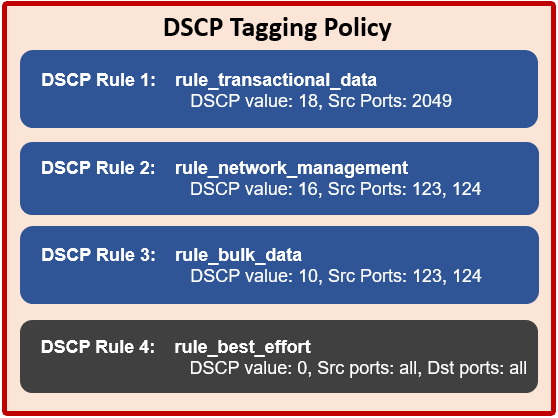
The OneFS DCSP implementation includes four default tagging rules:
| Class | Traffic | Default DSCP Value | Source Ports | Destination Ports |
| Transactional | File Access and Sharing Protocols:
NFS, FTP, HTTPS data, HDFS, S3, RoCE Security and Authentication Protocols: Kerberos, LDAP, LSASS, DCE/RPC RPC and Inter-Process Communication Protocols: rpc.bind, mountd, statd, lockd, quotd, mgmntd Naming Services Protocols: NetBIOS, Microsoft-DS |
18 | 20, 21, 80, 88, 111, 135 137, 138, 139, 300, 302, 304, 305, 306, 389, 443, 445, 585, 636, 989, 990, 2049, 3268, 3269, 8020, 8082, 8440, 8441, 8443, 9020, 9021 | Not defined by default, but administrator may configure. |
| Network Management | WebUI, SSH, SMTP, syslog, DNS, NTP, SNMP, Perf collector, CEE, alerts | 16 | 22, 25, 53, 123, 161, 162, 514, 6514, 6567, 8080, 9443, 12228 | Not defined by default, but administrator may configure. |
| Bulk Data | SmartSync, SyncIQ, NDMP | 10 | 2097, 2098, 3148, 3149, 5667, 5668, 7722, 8470, 10000 | Not defined by default, but administrator may configure. |
| Catch-All | All other traffic that does not match any of the above | 0 | all | Not defined by default, but administrator may configure. |
The ‘isi network firewall dscp list’ command can be used to view all of a cluster’s DSCP firewall rules. For example:
# isi network firewall dscp list DSCP Rules in Priority Order From High To Low: ID Description DSCP Value Src Ports Dst Ports ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ rule_transactional_data DSCP Rule for transactional data 18 20 - 21 80 88 111 135 137 138 139 300 302 304 305 306 389 443 445 585 636 989 990 2049 3268 3269 8020 8082 8440 8441 8443 9020 9021 20049 rule_network_management DSCP Rule for network management 16 22 - 25 53 123 161 162 514 6514 6567 8080 9443 12228 rule_bulk_data DSCP Rule for bulk data 10 2097 - 2098 3148 3149 5667 5668 7722 8470 10000 rule_best_effort DSCP Rule for best effort 0 all all ------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Total: 4
If desired, the ‘isi network firewall dscp modify’, followed by the appropriate rule name, can be used to modify a rule’s associated DSCP value, source ports, or destination ports. For example:
# isi network firewall dscp modify rule_transactional_data –src-port 123 –dst-ports 456 –dscp-value 10
Note that a ‘–live’ option is also available to effect the changes immediately on active rules. If the –live option is used when DSCP is inactive, the command is automatically rejected.
If needed, all of the DSCP configuration can be easily reset to its OneFS defaults and DSCP disabled as follows:
# isi network firewall reset-dscp-setting This command will reset the global firewall DSCP setting to the original system defaults. Are you sure you want to continue? (yes/[no]): yes
GUI-wise, DSCP has a new ‘settings’ tab under the WebUI’s firewall section for managing its operation and configuration, and editing the rules:
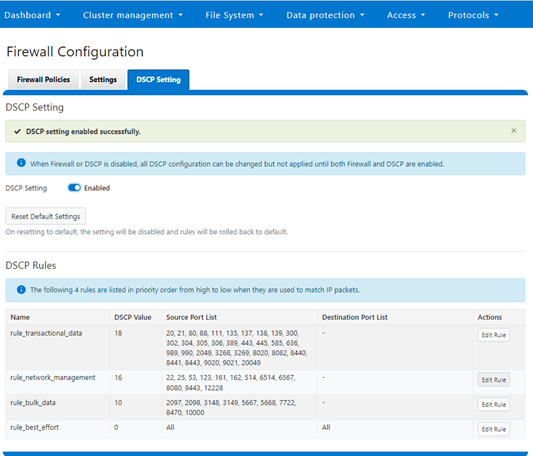
Again, although the DSCP feature can be configured and enabled with the firewall itself still disabled, DSCP will only activate once the firewall is up and running too.
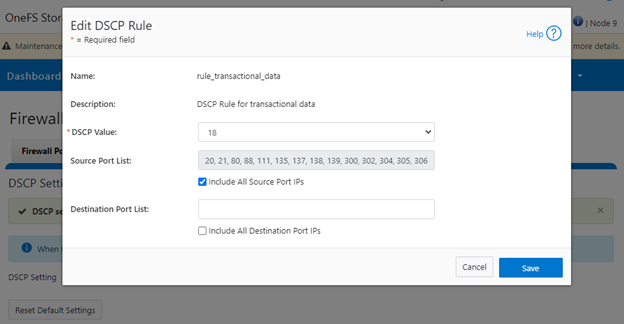
The WebUI allows modification of a rule’s associated DSCP value, source ports, or destination ports. For example:
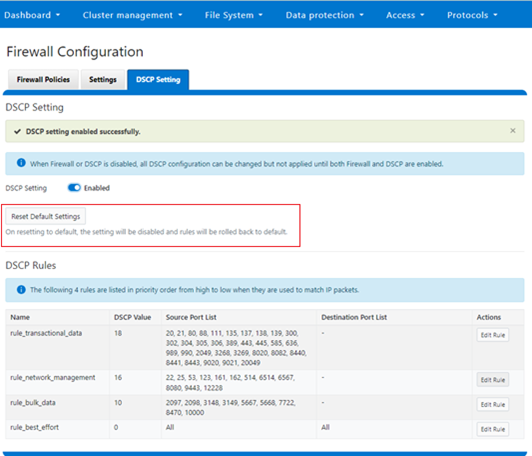
Like the CLI, the WebUI also has a ‘Reset Default Settings’ option which clears all the current DSCP configuration parameters and resets them to the OneFS defaults:
Also, there’s a comprehensive set of RESTful platform API endpoints, which include:
- GET/PUT platform/network/firewall/settings
- POST platform/network/firewall/reset-dscp-setting?live=true
- GET platform/network/firewall/dscp
- PUT platform/network/firewall/dscp/<rule_name>?live=true
All DSCP’s configuration data is stored in gconfig at the cluster level, and all the firewall daemon instances across the nodes work as peers. So if it becomes necessary to troubleshooting QoS and tagging, the following logs and utilities are a great place to start.
- /var/log/isi_firewall_d.log, which includes information from the Firewall daemon.
- /var/log/isi_papi_d.log, which covers all the command handlers, including the firewall and DSCP related ones.
- ‘isi_gconfig -t firewall’ utility, which returns all the firewall’s configuration info.
- ‘ipfw show’ command, which dumps the kernel’s ipfw table.
Also note that all these logs and command outputs are included in a standard isi_gather_info log collection.