Auditing can detect potential sources of data loss, fraud, inappropriate entitlements, access attempts that should not occur, and a range of other anomalies that are indicators of risk. This can be especially useful when the audit associates data access with specific user identities.
In the interests of data security, OneFS provides ‘chain of custody’ auditing by logging specific activity on the cluster. This includes OneFS configuration changes plus NFS, SMB, S3, and HDFS client protocol activity, which are required for organizational IT security compliance, as mandated by regulatory bodies like HIPAA, SOX, FISMA, MPAA, etc.
OneFS auditing uses Dell EMC’s Common Event Enabler (CEE) to provide compatibility with external audit applications.
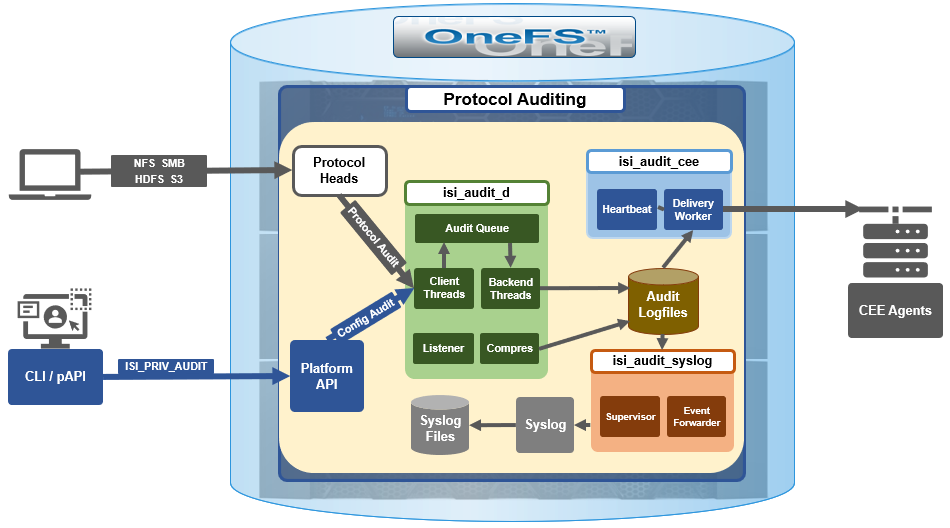
A cluster can write audit events across up to five CEE servers per node in a parallel, load-balanced configuration. This allows OneFS to deliver an end to end, enterprise grade audit solution which efficiently integrates with third party solutions like Varonis DatAdvantage.
OneFS auditing provides control over exactly what protocol activity is audited. For example:
- Stops collection of unneeded audit events that 3rd party applications do not register for
- Reduces the number of audit events collected to only what is needed. Less unneeded events are stored on ifs and sent off cluster.
OneFS protocol auditing events are configurable at CEE granularity, with each OneFS event mapping directly to a CEE event. This allows customers to configure protocol auditing to collect only what their auditing application requests, reducing both the number of events discarded by CEE and stored on /ifs.
The ‘isi audit settings’ command syntax and corresponding platformAPI are used to specify the desired events for the audit filter to collect.
A ‘detail_type’ field within OneFS internal protocol audit events allows a direct mapping to CEE audit events. For example:
“protocol":"SMB2", "zoneID":1, "zoneName":"System", "eventType":"rename", "detailType":"rename-directory", "isDirectory":true, "clientIPAddr":"10.32.xxx.xxx", "fileName":"\\ifs\\test\\New folder", "newFileName":"\\ifs\\test\\ABC", "userSID":"S-1-22-1-0", "userID":0,
Old audit events are processed and mapped to the same CEE audit events as in previous releases. Backwards compatibility is maintained with previous audit events such that old versions ignore the new field. There are no changes to external audit events sent to CEE or syslog.
- New default audit events when creating an access zone
Here are the protocol audit events:
| New OneFS Audit Event | Pre-8.2 Audit Event |
| create_file | create |
| create_directory | create |
| open_file_write | create |
| open_file_read | create |
| open_file_noaccess | create |
| open_directory | create |
| close_file_unmodified | close |
| close_file_modified | close |
| close_directory | close |
| delete_file | delete |
| delete_directory | delete |
| rename_file | rename |
| rename_directory | rename |
| set_security_file | set_security |
| set_security_directory | set_security |
| get_security_file, | get_security |
| get_security_directory | get_security |
| write_file | write |
| read_file | read |
| Audit Event |
| logon |
| logoff |
| tree_connect |
The ‘isi audit settings’ CLI command syntax is a follows:
Usage: isi audit <subcommand> Subcommands: settings Manage settings related to audit configuration. topics Manage audit topics. logs Delete out of date audit logs manually & monitor process. progress Get the audit event time.
All options that take <events> use the protocol audit events:
# isi audit settings view –zone=<zone> # isi audit settings modify --audit-success=<events> --zone=<zone> # isi audit settings modify --audit-failure=<events> --zone=<zone> # isi audit settings modify --syslog-audit-events=<events> --zone=<zone>
When it comes to troubleshooting audit on a cluster, the ‘isi_audit_viewer’ utility can be used to list protocol audit events collected.
# isi_audit_viewer -h Usage: isi_audit_viewer [ -n <nodeid> | -t <topic> | -s <starttime>| -e <endtime> | -v ] -n <nodeid> : Specify node id to browse (default: local node) -t <topic> : Choose topic to browse. Topics are "config" and "protocol" (default: "config") -s <start> : Browse audit logs starting at <starttime> -e <end> : Browse audit logs ending at <endtime> -v verbose : Prints out start / end time range before printing records
The new audit event type is in the ‘detail_type’ field. Additionally, any errors that are encountered while processing audit events, and when delivering them to an external CEE server, are written to the log file ‘/var/log/isi_audit_cee.log’. Additionally, the protocol specific logs will contain any issues the audit filter has collecting while auditing events.
These protocol log files are:
| Protocol | Log file |
| HDFS | /var/log/hdfs.log |
| NFS | /var/log/nfs.log |
| SMB | /var/log/lwiod.log |
| S3 | /var/log/s3.log |
Note that, on large clusters were there is heavy 100,000 of audit writes, when running the isi_audit_viewer utility across the cluster with ‘isi_for_array’, it can potentially lead to memory and other issues – especially if outputting to a directory under /ifs. As such, consider directing the output to an non-IFS location such as /var/temp. Also, the isi_audit_viewer ‘-s’ (start time) and ‘-e’ (end time) flags can be used to limit a search (ie. for 1-5 minutes), helping reduce the size of data.